To learn more about Bitcoin
What is Bitcoin?
It is rare to read a newspaper or a magazine without seeing Bitcoin mentioned these days. Bitcoin has grabbed the attention of people worldwide and interest in it continues to grow. It is also popular with those looking for a less mainstream method to conduct transactions. However, only some have an in-depth understanding and appreciation of its workings and potential.
With how often Bitcoin is discussed there is the danger of a "bandwagon effect." That is, people and organizations may be eager to use it without a total understanding. This article provides further insight into Bitcoin.
In its simplest form, Bitcoin allows for peer-to-peer transfer of electronic cash. This can already be accomplished using bank wires or banking apps, but that requires using a bank in the middle of the transaction, which can be time-consuming and frustrating. Peer-to-peer is direct, there is no need for an organization in the middle, and money can be transferred anywhere. Bitcoin can also be transferred across borders without roadblocks or reporting obligations.
The origin of Bitcoin
While some own Bitcoin, not everyone has a thorough understanding of where the underlying value comes from. Bitcoins are mined through a very difficult mathematical transaction process. As each new coin is mined, the math becomes harder so it is more and more difficult to mine additional coins. There is an absolute top end of 21 million Bitcoins allowed by the algorithms. While that sounds limiting, each Bitcoin can be sub-divided. It can be sub-divided into parts as small as one-hundred-millionth — known as a "Satoshi." However, with it being a limited resource, the scarcity drives the valuation.
At one time mining Bitcoins was an easy process if using a fast computer, but that is no longer the case. As the mathematics become continually more complex, the mining now requires many resources and is not profitable unless done in an area with very inexpensive electricity. Otherwise, the electricity costs of running a computer to mine for Bitcoins exceeds the value of what can be mined.
Bitcoin investment risks
Even the most ardent Bitcoin supporter must admit that Bitcoin is a volatile investment. There are some who regularly use Bitcoin for certain monetary transactions, while others understand the inner workings of Bitcoin and the scarcity created by the algorithms, viewing it as a reasonable investment opportunity. Unfortunately, some Bitcoin investors are intrigued by rising price graphs and the opportunity to make money. This could be a sign of a bubble as some are only investing for the opportunity and do not fully understand what they are buying. Think back to Holland's Tulip mania during the 1600s.
A Bitcoin crash could be worse than tulips and, without doubt, worse than a housing crash. Even if a house's value takes a significant dip, it is still a place to live. There is no intrinsic value to Bitcoin and no government or company guarantees it. Its value is only maintained due to demand.
Public sector organizations should be cautious
Currently, the focus of cryptocurrencies seems to be an investment vehicle, but this could shift over time. It is expected that cryptocurrencies will gain traction as instruments for transactions, though Bitcoin is not ready for public sector organizations.
Public sector organizations should be cautious about Bitcoin for the following reasons:
- It is anonymous (technically pseudo-anonymous)
- The price is highly volatile
- It is not popular with senior governments and tax authorities
- It is not backed by any government
- There is no recourse for fraud or theft
Bitcoin's anonymity
For many users, the anonymity Bitcoin offers is one of its most significant positive factors. Every user involved can see each transaction through the blockchain, which may not sound very anonymous. However, only the usernames (technically their crypto keys) are visible and the keys are anonymous. This is what it means to be pseudo-anonymous. The username who received or sent the funds is known, but the entity behind the username cannot be identified.
The anonymity of transaction partners can create uncertainty in the public sector for the following reasons:
- The vendor being paid is unknown unless they explicitly share their public key
- It could be helping the vendor create an off-book transaction
- It is difficult to know if the money is staying in Canada or going elsewhere
- The source of the money is unknown and could be linked to money laundering
Price volatility
The price swings in Bitcoin value have been dramatic as there have been periods of sharp increase and steep decline. The graph below depicts Bitcoin's value from 2012 to 2017.
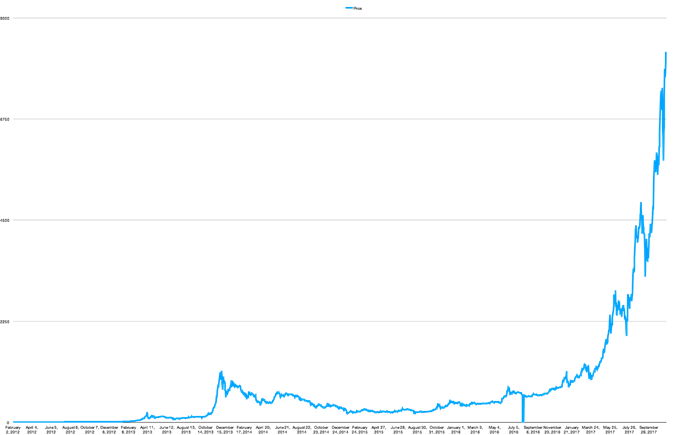
Below is an enhancement from early September 2017 when the price dropped 34% over a week.
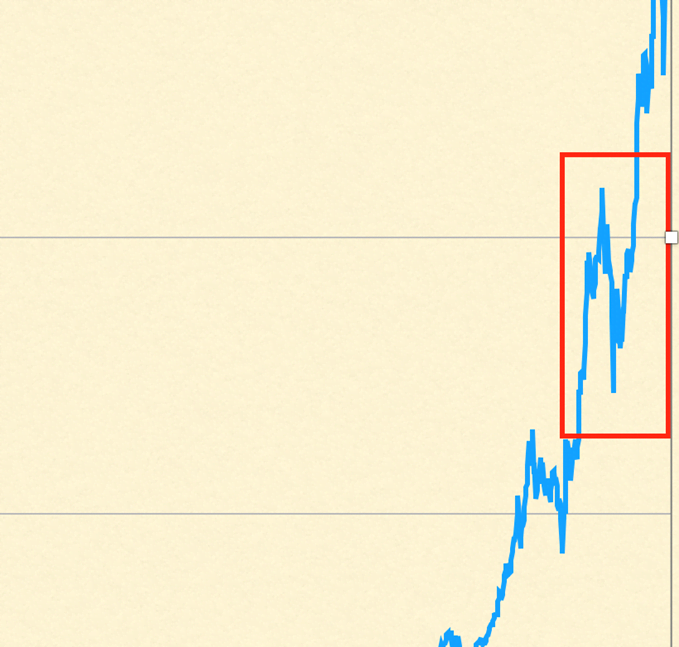
The Bitcoin price has recovered from the September 2017 setback and other setbacks. There is still concern about how increased government regulation would affect price and overall price volatility. Public sector entities tend to operate in a prudent and conservative manner — which would be difficult while using Bitcoin.
Governments and tax authorities
Senior governments and tax authorities might be apprehensive about Bitcoin for the following reasons:
- It can be difficult to determine if money is crossing borders
- There is uncertainty about how such transactions should or could impact money supply
- It cannot be determined whether income from transactions is being reported
- There is no audit trail beyond block-chain
Public sector organizations should consider concerns from senior government and tax authorities. As part of the government peer group, these organizations should lead by example and be good corporate citizens.
Bitcoin lacks government backing
The lack of government backing is the most problematic aspect of Bitcoin. The value of Bitcoin is the result of a general agreement that the increasingly difficult algorithm has value. If that were to change, or if other crypto-currencies take precedence, the value of Bitcoin could drop to zero. Consider what happened to MySpace once Facebook became the more popular social media platform. MySpace was once valued at over $12 billion, but when sold in 2011 the proceeds were only $35 million. Could something similar happen to Bitcoin? Not only is there no government backing of Bitcoin, there is no central authority of any kind. With no central authority for recourse, it can create a difficult situation if things go wrong. These risks may be acceptable for knowledgeable investors, but they are too high for the public sector.
Recourse for fraud or theft
Security is one of the most important elements of blockchain technology. The cutting-edge cryptography cannot be hacked if implemented properly. There is also no central database of transactions that can be hacked. Instead, all the ledger details are copied to transaction participants across the globe. While this distribution means the transaction data cannot be hacked, it is not completely safe.
The security design is laudable, but there are still weak points. The Mt. Gox theft of 850,000 bitcoins (more than US$500 million) is the most famous case. Mt. Gox involved the hack of Bitcoins at rest in the Mt. Gox digital wallet, rather than hacking transactions. With information technology, humans are the most significant weak link as they are subject to phishing and other social engineering attacks. The problem is, once a fraudulent transaction occurs there is a perfect record of it — but no recourse.
Recommendations
The technology is new and exciting, but the inherent risks in transacting in this environment are too high for public sector organizations. Further, widespread Bitcoin use could have a significant negative impact on government revenues. For these reasons, there are two overriding recommendations to consider:
- Be wary of accepting or promoting Bitcoin
- If involved in a transaction with Bitcoin, convert it to CDN$ as soon as possible
Meanwhile, monitor this emerging technology area. In particular, blockchain technology looks poised to enter the mainstream in the near future and many industry pundits are predicting it will be one of the most disruptive technologies. It will likely change banking and many other industries as well.